
To generate a barcode, you need to decide how many items you need barcodes for, order barcodes through GS1, and then apply the printed barcodes to your products.
Jump to:
In inventory management, tracking is of the utmost importance. Especially if your business is moving large quantities of stock, it’s pivotal to know where everything is during each part of the inventory management process.
Determining how to get a barcode for a product is an essential step for condensing product information in a single solution while keeping tabs on where products are in a warehouse. Barcodes use numbers, patterns, and parallel lines to create a readable code that machines can scan. Within this code, you can house all sorts of product information — like price, quantity, date of manufacture, and expiration dates for perishable goods.
Using barcodes is paramount in moving away from inventory chaos, achieving flow, and improving your inventory turnover ratio. When you adopt barcodes for your products, you can better control your stock while making more informed inventory decisions — regardless of how much inventory is in your warehouse.
In five easy steps, we’ll show you how to get barcodes for your products and the benefits of doing so.

1. Determine what type of barcode you need
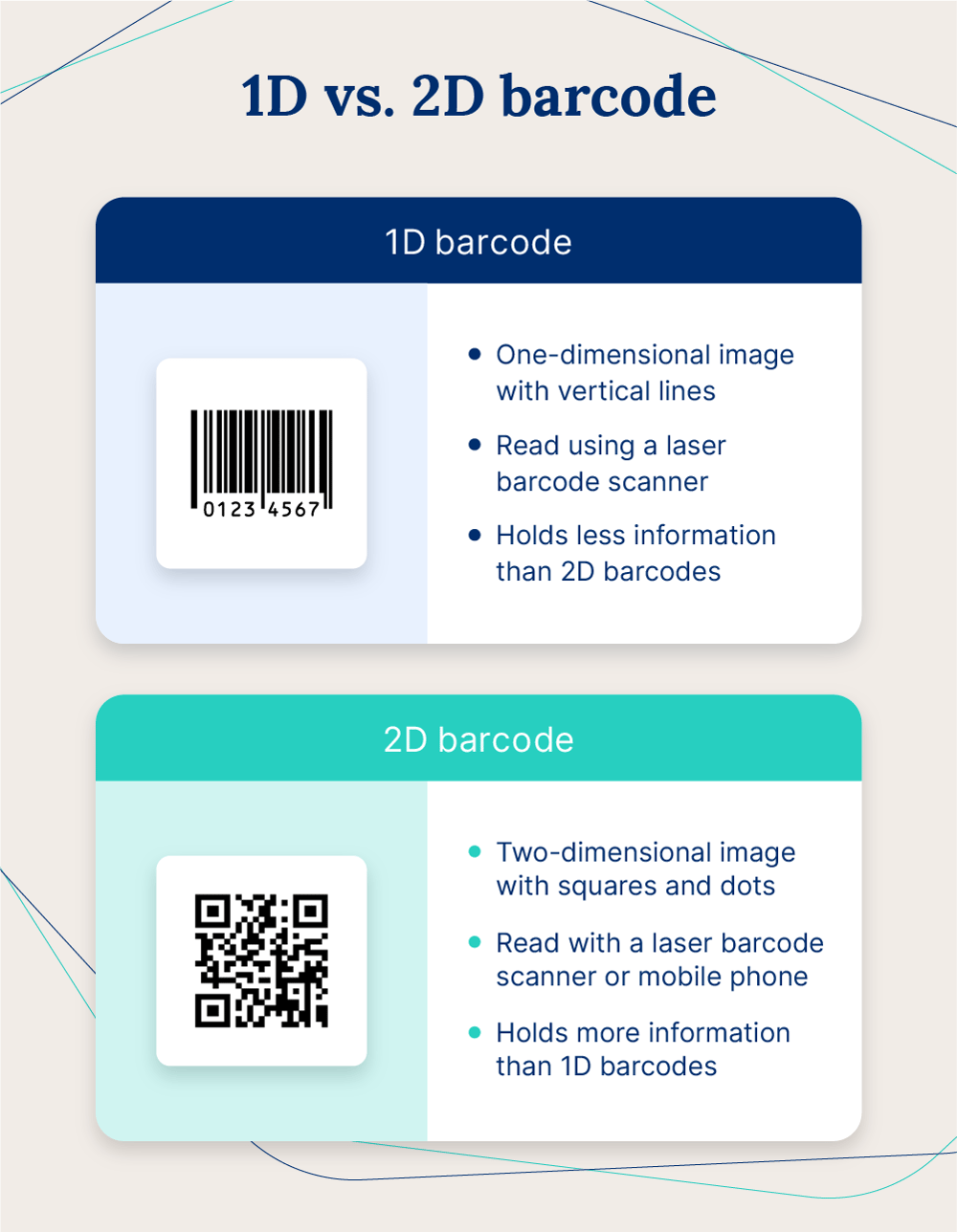
When getting barcodes for your products, you’ll typically choose between two different types. While there are additional types of barcodes that fall within these two groups, the main two categories of barcodes are:
- 1D (linear) barcodes
- 2D barcodes
1D barcodes are the most common and traditional type of barcode and generally appear on packaging. 2D barcodes are a more recent advancement and can hold more information than 1D codes. QR codes, for example, are a type of 2D barcode that many companies widely use.
2. Check how many products require barcodes
Your next step is to see how many products you’ll need to get barcodes for, as this will help you determine if you want to use a barcode issuing organization, like GS1, or generate them yourself.
GS1 is a global barcode issuing organization — preferred by companies because of their barcode standards and their use of company prefixes or unique numbers given to your company by GS1.
For example, going through an issuing organization makes more sense if you’re a business owner dealing with your store’s inventory. If you use GS1, you’re guaranteed a unique barcode for all of your products, whereas if you generate it through an online generator, you may receive a replica. Without a unique barcode, you won’t be able to track your product properly.
If you’re striving to build a professional retail business, use GS1. Note, however, that the number of products you need barcodes for will dictate the initial and annual fee that you pay GS1 for your barcodes. The price of barcodes breaks down like this:
| GS1 pricing table | ||
| Number of items | Initial fee | Annual fee |
| 1 item | $30 | No annual fee |
| 10 items | $250 | $50/year |
| 100 items | $750 | $150/year |
| 1,000 items | $2,500 | $500/year |
3. Create a GS1 account
Assuming that you’re using GS1 to create your barcodes, the next step is to create a GS1 account.
Once you navigate to the GS1 website, it only takes a few steps to begin generating your barcodes. Simply create an account through the website and then fill out sections about your product. From there, GS1 will handle the rest for you.
4. Obtain unique identification numbers for your products
Once you’ve created your GS1 account and registered your products, you’ll be given Global Trade Item Numbers (GTINs) — unique identification numbers for your products.
These numbers follow your company prefix and will appear on the barcodes you will eventually apply to your product packaging. Typically, a GTIN will be 12 digits and appear under the barcode’s parallel lines.
5. Add the barcodes to product packaging and test for accuracy
After generating and printing your barcodes, it’s time to apply them to your product packaging or directly to your products.
As a final checkpoint, testing your barcodes to ensure they’re housing the correct product information is beneficial. Before shipping products off, scan your products to ensure they’re correct. Inaccurate product information can cause setbacks and slow down your inventory control process.
Printing Labels with barcodes
Types of barcodes
There are different types of barcodes, so it’s up to you to determine which is best for your business.
1D and 2D barcodes are the two major types of barcodes, but many popular barcode types fall within these categories. Two of these include:
UPCs
UPCs, or Universal Product Codes, are the most common type of 1D, or linear, barcodes and are seen largely on product packaging. Assigned exclusively by GS1, all barcode scanners can read UPCs and they provide a unique GTIN for all of your products.
UPCs are an excellent choice for housing basic product information, but they cannot hold as much information as a 2D barcode, like a QR code. UPCs typically contain:
- The GS1 company prefix (the first six to 10 digits)
- The item number (the next one to five digits)
- The check digit (the last digit)

QR codes
QR (Quick Response) codes are 2D barcodes companies use to house more information than a linear barcode can. Using a QR code comes with several added benefits:
- Can be scanned by smartphones and tablets, while 1D barcodes can only be read by barcode scanners
- Can be created with a free online generator, without having to rely on an issuer for unique GTINS
As a result, specific industries prefer using QR codes for customer service, POS systems, and inventory tracking. Restaurants and bars, for instance, leverage QR codes for contactless ordering and payments. Food and beverage companies can also use QR codes to house comprehensive nutrition information for their products.
How do barcodes benefit small businesses?
Leveraging barcodes can be vital in your larger inventory and order management process. By using barcodes, you can better manage product information, easily track stock, and reduce the amount of chaos in your inventory cycle. Here are a few more advantages of generating barcodes for your products:
Streamlined inventory management
By using barcodes, small businesses can easily track inventory moving in and out of warehouses. If you manage multiple locations or warehouses in different places, using barcodes is the best way to centralize product data in one place so you can keep tabs on all your locations.
The best warehouse management systems come equipped with barcode scanning for these reasons. Cin7 Core uses barcode scanning in its warehouse management app so you can easily track stock from receiving to shipping.
Try Cin7’s Warehouse Management System today.
Reduced errors
Barcodes additionally allow you to keep an accurate record of how much stock you have on hand. By using GTINs for each product, you can easily see what’s in stock simply by scanning the barcode.
When performing inventory cycle counts, it can cause major setbacks if you find physical inventory isn’t matching records. Using barcodes allows you to maintain a more accurate record of what’s in your warehouse.
Enhanced efficiency
On the customer side, barcodes create a more efficient checkout process, allowing you to quickly funnel customers in and out of your store.
Restaurants, for example, can leverage on-table QR codes for quick and contactless payments, allowing them to turn over customers and fill seats more efficiently.
Frequently asked questions
If you’ve still got questions about how to get a barcode for a product, here are a few common questions and answers about obtaining barcodes for your products.
How much does it cost to get a barcode for a product?
The price of barcodes depends on the number of products you need barcodes for. If using GSI, the prices break down as so:
| Number of items | Initial fee | Annual fee |
| 1 | $30 | No annual fee |
| 10 | $250 | $50 |
| 100 | $750 | $150 |
| 1,000 | $2,500 | $500 |
Do you need a barcode to sell in stores?
You don’t necessarily have to have barcodes for your products to sell them in stores. However, using barcodes helps you track inventory, better keep track of sales and inventory quantity, and allow your store to appear more professional.
Can you create your own barcodes?
You can create your barcodes through online generators, but you’ll need to use GS1 to obtain GSINs or unique identification numbers. Your barcodes may be identical to other online-generated ones if you use a free tool.
Is there a difference between SKUs and barcodes?
SKUs and barcodes are similar in that they’re used to describe products but have slightly different use cases. While barcodes are machine-readable codes that hold product information, SKUs are alphanumeric designators that describe a product’s features, like color and size.
Every product has a unique SKU so the seller can easily tell them apart. Barcodes rephrase the information designated in an SKU so it can be easily identified when the product is scanned.
Do you need barcodes for SKUs?
You don’t need a barcode for your SKU, but companies often create barcodes for SKUs to streamline the inventory management process. Generating a barcode for your SKU allows you to quickly and easily update product information just by scanning the barcode.
Who gives a barcode for a product?
GS1 is the global issuer of barcodes for products. If you’re running a business and need barcodes, you’ll create a GS1 account and obtain your barcodes through their website.
How do I generate a barcode for my products?
For most businesses, the best way to generate barcodes will be through GS1. However, once you have barcodes for your products, leveraging inventory management software equipped with barcode scanning can help you make the most of your investment and manage your inventory more efficiently.
Cin7 Core’s warehouse management feature uses barcode technology for easy picking and packing — so your inventory can manage itself.
Start a free trial of Cin7 to grow your business today.
More from the blog
View All Posts
What is working capital, and why should SMBs care about it?
Read More
Top 10 Inventory Management Rules for Your Business
Read More


